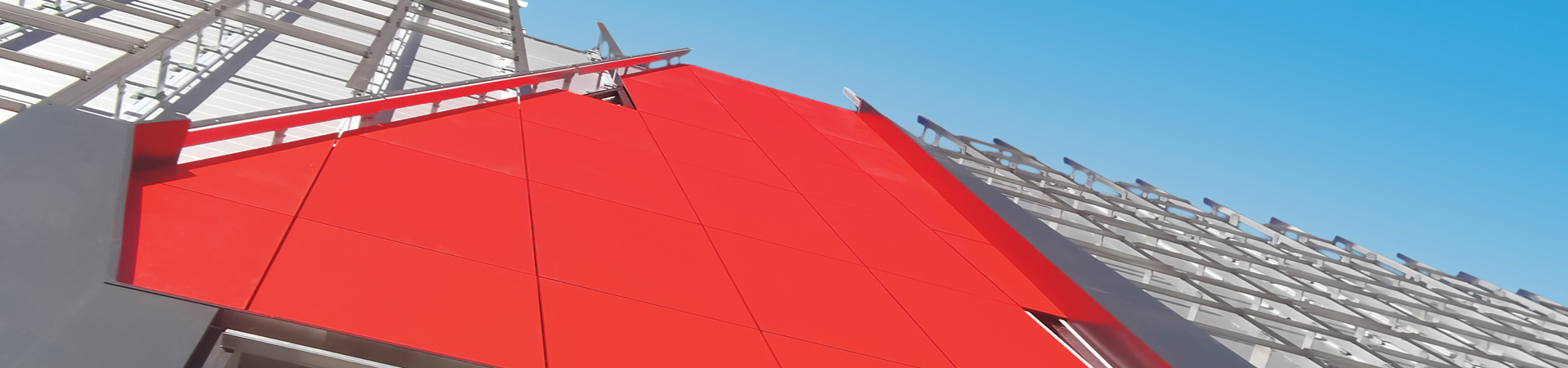
Specifying cladding attachment systems
Course Number SFS001
LU 1 LU/Elective
Category/Sub-category Building systems, materials, & assemblies
Expiration 04/26/2025

With increasing requirements for the building enclosure in energy codes, many building projects are moving towards using exterior insulated building assemblies. Exterior insulated systems allow for increased thermal performance but much of that depends on the design of the exterior cladding attachment system. There are a wide variety of secondary structural attachment systems in the North American market competing to provide better thermal performance, which can overwhelm designers when comparing them for use on projects.
While direct comparisons of components ("clip to clip") may show two systems to be equivalent, it is not until additional project requirements are compared that significant differences in performance can arise. These additional requirements include structural considerations, like wind and dead loads, which dictate the spacing of components, combustibility restrictions on components, and installation flexibility. The perceived advantages in performance from one system over another may not actually turn into tangible benefits once these other design requirements on the project are also satisfied.
The intent of the presentation will be to provide the necessary background information, methodologies and available resources to guide designers in making informed decisions for selecting the right cladding attachment systems for their projects.
While direct comparisons of components ("clip to clip") may show two systems to be equivalent, it is not until additional project requirements are compared that significant differences in performance can arise. These additional requirements include structural considerations, like wind and dead loads, which dictate the spacing of components, combustibility restrictions on components, and installation flexibility. The perceived advantages in performance from one system over another may not actually turn into tangible benefits once these other design requirements on the project are also satisfied.
The intent of the presentation will be to provide the necessary background information, methodologies and available resources to guide designers in making informed decisions for selecting the right cladding attachment systems for their projects.
 English (Canada)
English (Canada)
 čeština (Česká republika)
čeština (Česká republika)
 magyar (Magyarország)
magyar (Magyarország)
 Deutsch (Deutschland)
Deutsch (Deutschland)
 eesti (Eesti)
eesti (Eesti)
 español (España)
español (España)
 português (Portugal)
português (Portugal)
 suomi (Suomi)
suomi (Suomi)
 français (France)
français (France)
 English (United Kingdom)
English (United Kingdom)
 italiano (Italia)
italiano (Italia)
 Nederlands (Nederland)
Nederlands (Nederland)
 norsk, bokmål (Norge)
norsk, bokmål (Norge)
 polski (Polska)
polski (Polska)
 svenska (Sverige)
svenska (Sverige)
 Türkçe (Türkiye)
Türkçe (Türkiye)

